Stichwortverzeichnis - Implantologie
A / BAbdruck - Kapitel 10.2
Abstoßung - Kapitel 12.1
Abutment
AIDS
Alloplastisch - Kapitel 12.1
Alveole
Anamnese - Kapitel 7
Antibiotikum - 11.1
Aplasie
Arrhythmie
Arteriosklerose
Artikulation - Kapitel 1
Aseptisch
Atrophie - Kapitel 6
Aufklärung .
Augmentation - Kapitel 12 ff.
Autogen - Kapitel 12.1
Beckenkamm - Kapitel 12.1
Biokompatibilität - Kapitel 12.1, 14
Bohrschablone - Kapitel 7 ff., 10.2.2,10.2.4
C / DCAD - Kapitel 10.2.4
Chirurgischer Eingriff - Kapitel 1, 11, 14
Computertomografie - Kapitel 7, 10.2.2
Cortison
Dental - Kapitel 3 ff.
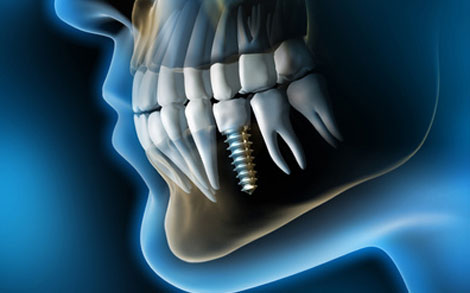
Dentale Implantate - Kapitel 3 ff.
Diabetes mellitus
Diagnostik - Kapitel 10.2 ff
Diagnostische Bohrschablone - Kapitel 10.2.2
Digitale Volumentomografie (DVT) - 10.2.2
Distraktionsosteogenese
E / FEndokarditis
Enossal - Kapitel 3.2
Entzündung - 15
Extrahieren/Extraktion - Kapitel 3.3
Fachbegriffe - Kapitel 18
Folgen des Zahnverlustes - Kapitel 6
G / HGebührenordnung für Zahnärzte (GOZ) - Kapitel 16
Geschlossene Einheilung - Kapitel 3.4
Gesetzliche Krankenkasse - Kapitel 16
Gingiva.
Gingiva-Former 11.2
Gingivitis - Kapitel 3.3, 10.2.1
Gipsmodell - Kapitel 10.2
Heil- und Kostenplan - 16
Hepatitis
HIV
Hypertonie
I / J / KImmunsuppressiva
Implantat - Kapitel 3 ff.
Implantatbett - Kapitel 12 ff.
Implantatbruch - Kapitel 14
.
Implantatgestützt - Kapitel 3
Implantatinsertion - Kapitel 10.2.4, 11 ff.
Implantation - Kapitel 1 ff.
Implantationskosten - Kapitel 16
Implantationsmethode - Kapitel 3.4
Implantationszone
Implantatoberfläche - Kapitel 3.1
Implantatpfosten
Implantatprothetik - Kapitel 5.4
Implantatprothetisch - Kapitel 5.4
Implantatsystem - Kapitel 3.3
Implantattypen - Kapitel 3.2
Implantatverlust - Kapitel 15
Implantatwerkstoff - Kapitel 3.1
Implantieren - siehe Implantation
Implantologe - Kapitel 1 ff.
Implantologie - Kapitel 1
Implantologisch - Kapitel 11 ff.
Inlay - Kapitel 5.3
Insulin
Interdentalbürste - Kapitel 15
Intraoral
Karies
KEM 12 ff.
Kiefergelenk
Kieferknochen - Kapitel 3.4 ff.
Knochenatrophie - Kapitel 6
Knochenaufbau
Knochenaufbaumaterial - Kapitel 12.1
Knochenaugmentation
Knochenersatzmaterial (KEM) 12
Knochenschwund - Kapitel 6
Knochentransplantat
Komplikation - Kapitel 14
Kontraindikation (relative, absolute)
Kontrollen - Kapitel 15
Kosten - Kapitel 16
Kostenerstattung - Kapitel 16
Krankheitsgeschichte
Kühlmaske - Kapitel 11.2
L / M / NLaser-Chirurgie
Lokalanästhesie - Kapitel 11
Lückenhalter
Membran - Kapitel 12.1
Minimal-invasiv - Kapitel 7
Mitarbeit des Patienten - Kapitel 15
Modellanalyse - Kapitel 10.2.3
Muko-Gingival-Grenze
Mukosa
Mundhöhle - Kapitel 10.2.1
Mundhygiene - 15
Navigierte Implantation - Kapitel 10.2.4
O / P / QOberkiefer - 10.2
Obstruktiv
Offene Einheilung - Kapitel 3.4
Operationsvorbereitung - Kapitel 11.1
Oralchirurg - Kapitel 1
Orthopantomogramm - Kapitel 10.2.2
Osteomyelitis
Osteoporose
Osteosyntheseschraube - Kapitel 12.1
Palpation - Kapitel 10.2.1
Panoramaröntgenaufnahme - Kapitel 10.2.2
Parodontitis - Kapitel 3.3, 5.4, 15
Patientenaufklärung -
Periimplantitis - Kapitel 15
Planung - Kapitel 10, 10.1
Präoperativ
Private Krankenversicherung - Kapitel 16
Privatleistung - Kapitel 16
Professionelle Zahnreinigung - 15
Prophylaxe - Kapitel 15
Prothese - Kapitel 5.3 ff.
Provisorium
Quellenangaben - Kapitel 19
R / SRadiofrequenzchirurgie
Risikoaufklärung -
Röntgen - Kapitel 10.2.2
Rotationssymmetrisch - Kapitel 3.2
Schleimhaut
Schmerzen - Kapitel 14
Schneider'sche Membran
-
Sinusbodenelevation
Socket Preservation
Sofortimplantat - Kapitel 3.3
Spätimplantat - Kapitel 3.3
Suprakonstruktion
T / UTeilprothese - Kapitel 5.3 ff.
Therapeutische Aufklärung
Therapeutische Bohrschablone - Kapitel 10.2.4
Transplantation - Kapitel 1, 12 ff.
Tumor
Ultraschall-Skalpell
Unfall - Kapitel 5
Unterkiefer - 10.2
V / WVorbereitung der Implantation - Kapitel 11.1
Weichgewebe
Wirtschaftliche Aufklärung
Wurzelspitzenresektion
X / Y / ZXenogen - Kapitel 12.1
Zahnbelag - Kapitel 15
Zahnextraktion - siehe Extraktion
Zahnfleisch - siehe Gingiva
Zahnhalteapparat - 15
Zahnimplantat - siehe Implantat
Zahnimplantation - siehe Implantation
Zahnimplantologe - siehe Implantologe
Zahnlosigkeit
Zahnlücken
Zahnpasta - Kapitel 15
Zahnseide - Kapitel 15
Zahnverlust - Kapitel 5 ff.
Zahnwurzel - Kapitel 1 ff.
Zahnzwischenräume - Kapitel 15
Zirkondioxid/Zirkonium - Kapitel 3.1
Zweizeitige Implantation - Kapitel 11.2
Zuletzt aktualisiert: 18.11.2013